

- #PUTTY SSH CERTIFICATE DRIVER#
- #PUTTY SSH CERTIFICATE VERIFICATION#
- #PUTTY SSH CERTIFICATE PASSWORD#
- #PUTTY SSH CERTIFICATE WINDOWS#
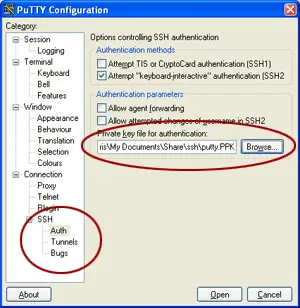
In the command line window, specify the username that you use for the SSH tunnel and press Enter. In the Private key file for authentication field, specify the path to your private key file and click Open. In the PuTTY Configuration dialog, navigate to Connection | SSH | Auth. Disable SSH connection to a databaseĬlick the SSH/SSL tab and clear the Use SSH tunnel checkbox.Ĭreate the SSH tunnel with PuTTY (Windows)ĭownload and run the latest version of the PuTTY SSH and Telnet client (download the client from ). See the Generating a new SSH key and adding it to the ssh-agent tutorial for details on working with SSH keys.
#PUTTY SSH CERTIFICATE WINDOWS#
OpenSSH config and authentication agent: to use SSH keys that are managed by a credentials helper application (for example, Pageant on Windows or ssh-agent on macOS and Linux). To have DataGrip remember the passphrase, select the Save passphrase checkbox. Specify the path to the file where your private key is stored and type the passphrase (if any) in the corresponding fields. DataGrip supports private keys that are generated with the OpenSSH utility. To apply this authentication method, you must have a private key on the client machine and a public key on the remote server. Key pair (OpenSSH or PuTTY): to use SSH authentication with a key pair.
#PUTTY SSH CERTIFICATE PASSWORD#
To save the password in DataGrip, select the Save password checkbox. Password: to access the host with a password. In Host, User name, and Port fields, specify your connection details.įrom the Authentication type list, you can select an authentication method: If you do not want to share the configuration between projects, select the Visible only for this project checkbox. Select a data source profile where you want to change connection settings.Ĭlick the SSH/SSL tab and select the Use SSH tunnel checkbox.Ĭlick the Add SSH configuration button ( ). If you do not want to share a connection between projects, select the Visible only for this project checkbox in the SSH connection settings. Secure Shell or SSH is a network protocol that is used to encrypt a connection between a client and a server.Īll created SSH connections are shared between all the data sources that you have in a project. If you configured SSL settings for one data source, you can copy them for another data source.Ĭlick the Copy from link and select the configuration that you want to copy.Īfter you have configured the SSH settings, on the General tab, use the host address and the database port, not localhost.
#PUTTY SSH CERTIFICATE DRIVER#
As a temporary solution, try to downgrade the JDBC driver (for example, for the MySQL connector, you need to switch to the 5.1.40 version.) Disable SSL connection to a databaseĬlick the SSH/SSL tab and clear the Use SSL checkbox.Ĭopy SSL settings from other data sources The SSL connection might fail if your Java keystore does not accept the certificate chains. With self-signed certificates and in some cases with certificates issued by the trusted root entity, you might experience errors when you use the latest JDBC driver version. It is recommended to use PEM certificates. To ensure that the connection to the data source is successful, click Test Connection. The SSL connection fails if the server certificate cannot be verified. Verify CA: verifies the server by checking the certificate chain up to the root certificate that is stored on the client.įull Verification: verifies the server host to ensure that it matches the name stored in the server certificate. Require: verifies that the server accepts SSL connections for this IP address and recognizes the client certificate.
#PUTTY SSH CERTIFICATE VERIFICATION#
In the Client key file field, navigate to the client key file (for example, client-key.pem).įrom the Mode list, select the verification mode: In the Client certificate file field, navigate to the client certificate file (for example, client-cert.pem). In the CA file field, navigate to the CA certificate file (for example, mssql.pem). On the Data Sources tab, select a data source that you want to modify.Ĭlick the SSH/SSL tab and select the Use SSL checkbox. In the Database Explorer ( View | Tool Windows | Database Explorer), click the Data Source Properties icon. You can open data source properties by using one of the following options:

See the Tutorials section that includes configuration examples for Apache Cassandra, Heroku Postgres, and MySQL 5.1. For some databases, you need to use another approach for a successful connection.

The following procedure describes the SSL configuration that suits most databases. To make a connection to a database more secure, some services require SSH or SSL usage.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
